
Corrosion is considered one of the main reasons why reinforced concrete and prestressed concrete structures deteriorate around the world. The number of RC buildings grows rapidly around the world and this is why demand for easily applicable, affordable maintenance programs grows as well.
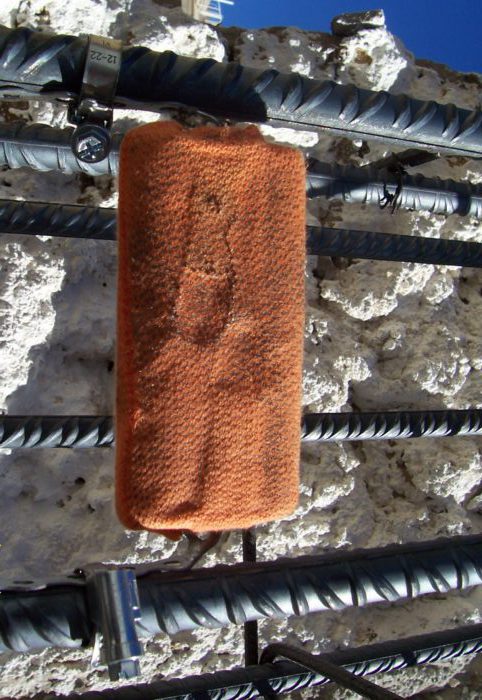
Cathode protection of reinforced concrete structures can be achieved through steel reinforcement polarization with direct current. To make it happen anodes are mounted, painted or embossed on the concrete surface and then connected to the positive pole of the DC power source in case of ICCP anodes or directly connected to steel reinforcement in case of galvanic anodes.
In galvanic cathode protection (GACP) the anode (normally zinc) delivers outside current for cathode protection. Liquids in the concrete pores (concrete pore solution) act as electrolyte and enable the flow of ions within the electric field created by the cathode protection system. The protection is sufficient if key areas of the structure meet specific protection criteria.
The GACP system using galvanic anodes is simple and reliable. Recently it has become a real alternative to ICCP. Contrary to ICCP, the GACP systems do not require extensive wiring, connections or power source. Their simplicity greatly reduces the needs regarding monitoring and maintenance.
The European ISO 1269 standard „Cathodic protection of steel in concrete” specifies performance requirements for cathodic protection in cement-based concrete. The purpose of cathodic protection of reinforced concrete is stopping the process of steel corrosion in concrete with impressed current.
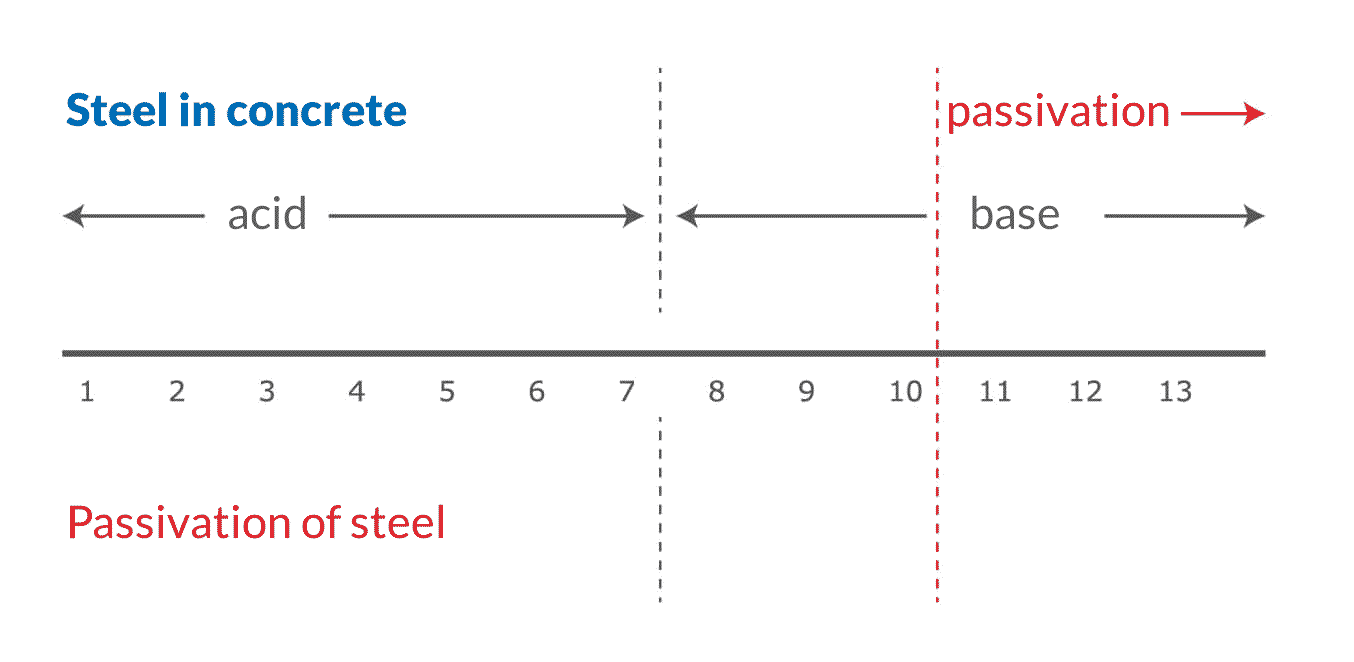
The presence of hydrochloric acids in concrete can pose danger to the passivating layer (protective oxide layer) that can be found in concrete-buried reinforcement steel. Also the varying thickness of concrete layer over reinforcement, concrete quality in this layer and presence of acids around the reinforcement will lead to emergence of similar corrosion conditions.
These conditions will lead to the emergence of local corrosion areas. These areas become anodes. Other areas on the reinforcement, where conditions are less corrosive and aggressive, continue to get passivized (passive oxide layer). These areas become cathodes.
KEY BENEFITS OF GALVANIC CATHODIC PROTECTION OF STEEL IN CONCRETE
It effectively extends the lifespan of reinforced concrete structures.
It leads to a significant reduction in maintenance costs.
Placing galvanic anode in concrete while erecting a new structure is very easy.
In new concrete structures the system requires fewer anodes per square meter, which further reduces costs.
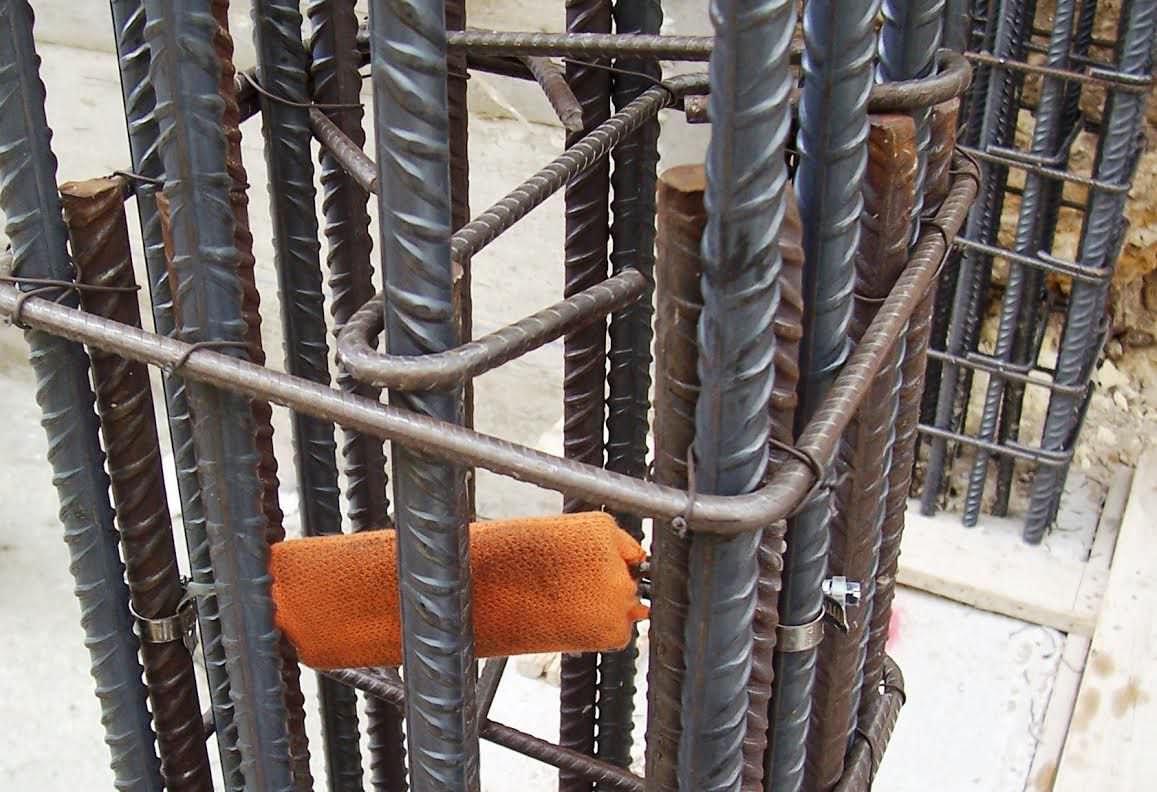

Excellent durability and protection efficiency.
Highly effective technology for preventing deterioration of reinforced concrete as a result of chlorine action and corrosion of carbon-containing concrete.

